
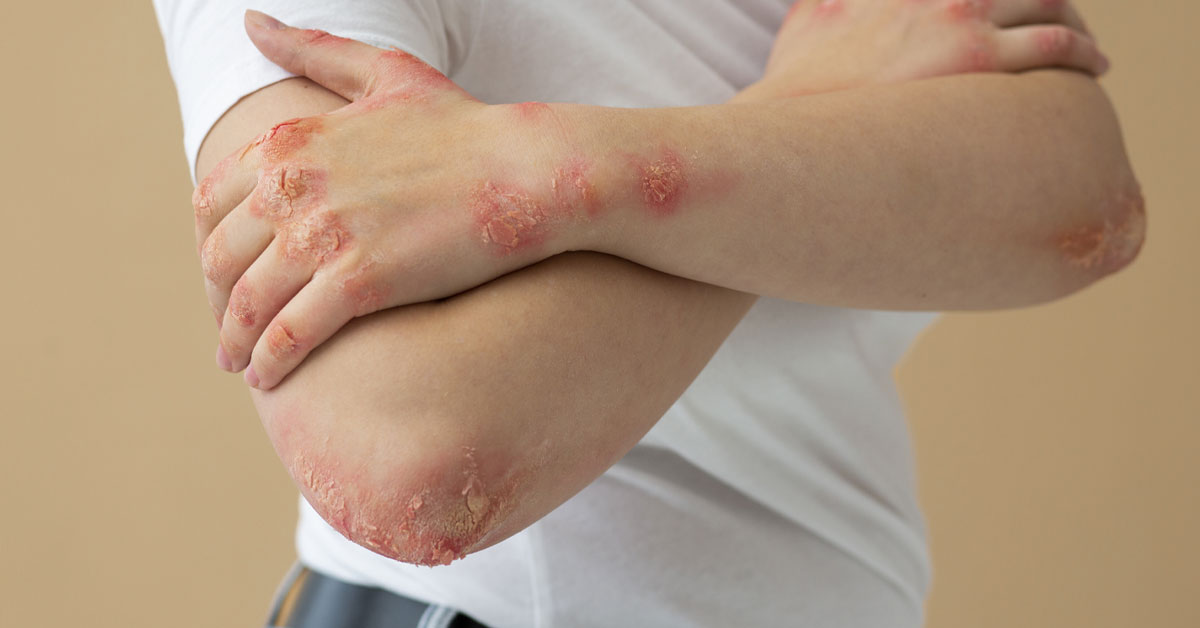
KATHMANDU: Allergic reactions occur when the immune system overreacts to substances called allergens that come into contact with the skin, nose, eyes, respiratory tract, or gastrointestinal system. Common allergens include poison ivy, fragrances, and medications, which can cause allergic rashes that vary in size and severity depending on their cause.
An allergic reaction happens when the immune system treats substances that are generally harmless as threats. Common allergens include mold, pollen, and certain foods.
There are four types of allergic reactions, each triggered differently and presenting distinct symptoms:
Type I (Immediate or Anaphylactic Reactions): These occur within minutes of exposure to an allergen.
Type II (Antibody-Dependent Reactions): These happen when the immune system attacks part of the body.
Type III (Immune Complex Reactions): Similar to Type II, but involve the immune system attacking other parts of the body.
Type IV (Delayed Hypersensitivity Reactions): These develop 12 to 72 hours after exposure to an allergen.
The exact causes of allergies remain unclear, but certain substances are commonly known to trigger allergic reactions. People who have allergies may be sensitive to one or more of the following:
Allergens can enter the body in several ways:
Several factors increase the likelihood of developing allergies, including:
Mild Allergic Reaction
Symptoms of a mild allergic reaction may include:
Severe Reaction
Severe allergic reactions, such as those triggered by food, insect stings, or medications, may cause:
A severe allergic reaction known as anaphylaxis can develop within seconds and can be life-threatening. Symptoms include:
Anaphylaxis requires immediate medical attention, as it can result in death without treatment.
If someone suspects they have an allergy, a doctor can help identify the allergen. The person should be prepared to explain:
Doctors may recommend tests such as:
While there’s no cure for allergies, treatments can help manage symptoms. The best way to manage an allergy is to avoid allergens, though this isn’t always possible.
Medication options include:
To prevent allergic reactions:
Possible complications from allergic reactions include: