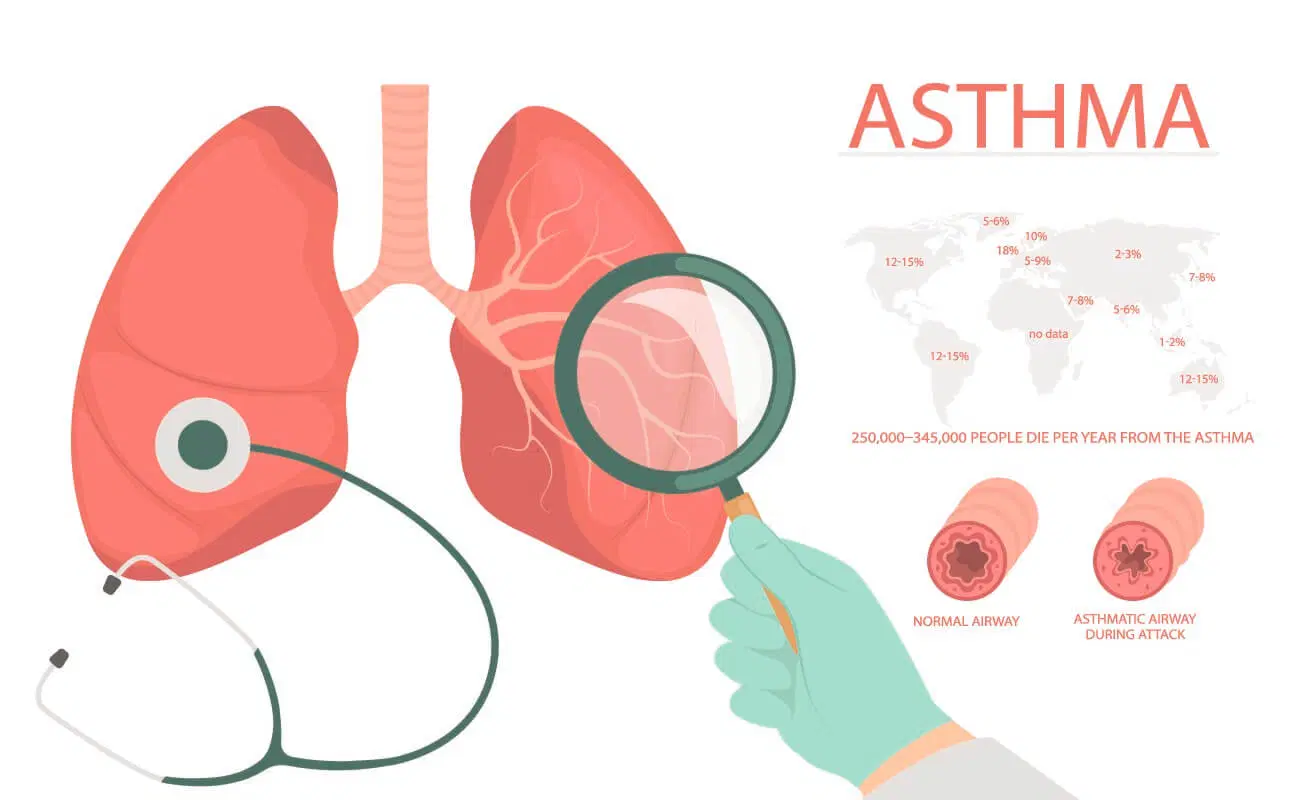
Asthma is a common chronic lung disease that causes inflammation in the airways (bronchial tubes) of the lungs.
In some cases, the primary symptom may be a persistent cough, particularly at night, or tightness, noisy breathing, and wheezing.
Asthma can resemble other respiratory conditions such as emphysema, bronchitis, or lower respiratory infections. The most common types of asthma include:
- Exercise-induced bronchospasm
- Allergic asthma
- Occupational asthma
- Cough-variant asthma
- Non-allergic asthma
- Nocturnal asthma (nighttime asthma)
Causes of Asthma
Several factors can trigger asthma, including:
- Tobacco smoke
- Outdoor air pollution
- Smoke from wood or other materials
- Respiratory infections
- Strong emotional states (fear, anxiety, depression, stress)
- Certain medications like NSAIDs (ibuprofen, naproxen)
- Specific foods and food additives (nearly any food can trigger an allergic reaction)
- Genetics
- A history of viral infections
Risk Factors for Asthma
Certain factors increase the risk of developing asthma:
- Exposure to tobacco smoke
- Living in urban environments
- A family history of asthma or other allergic conditions like eczema
- Personal medical history of allergies
- Genetics: Some genes predispose individuals to asthma by influencing immune system responses and airway inflammation
- Respiratory infections during early childhood, such as RSV (respiratory syncytial virus)
- Exposure to allergens like pollen, dust mites, pet dander, and cockroach droppings
- Occupational exposure to chemicals, fumes, or allergens
- Secondhand smoke exposure
- Air pollution
- Poor diet and lack of proper nutrition
- Obesity
- Living in urban environments with higher levels of pollution and allergens
Symptoms of Asthma
Common symptoms include:
- Coughing
- Throat clearing
- Wheezing
- Difficulty sleeping
- Chest tightness or pain
- Fatigue
If your symptoms worsen or don’t improve with an inhaler, seek immediate medical treatment. You should also seek treatment if you experience symptoms of an asthma emergency, such as:
- Difficulty walking or talking
- Confusion
- Gasping for air
- Severe trouble breathing
- Dizziness
Diagnosis of Asthma
To diagnose asthma, healthcare providers may use:
- Chest X-ray
- Blood tests
- Peak Flow Monitoring (PFM)
- Allergy tests
- Spirometry (a common test to measure lung function) to determine the severity of lung disease and monitor treatment effectiveness
Managing and Treating Asthma
- Identify and minimize exposure to asthma triggers
- Monitor symptoms to recognize when asthma is worsening
- Follow prescribed medication regimens
- Use inhalers to control asthma and maintain a normal, active life
Types of Inhalers
There are two main types of inhalers:
- Bronchodilators (e.g., salbutamol) that open air passages and relieve symptoms
- Steroids (e.g., beclometasone) that reduce inflammation in the airways, improving symptoms and reducing the risk of severe asthma attacks
Possible Complications of Asthma
Asthma complications can be severe and may include:
- Lack of sleep due to nighttime symptoms
- Permanent lung function changes
- Decreased ability to exercise or engage in activities
- Persistent cough
- Breathing difficulties that require assistance
- Death
Prevention of Asthma Symptoms
To help prevent asthma exacerbations:
- Avoid triggers such as smoke and strong odors
- Manage outdoor allergens and identify personal allergens
- Prevent respiratory infections, especially during cold and flu season
- Control indoor air quality by minimizing dust, using air purifiers, and managing humidity levels
- Promote a healthy pregnancy and childhood environment by avoiding early exposure to environmental toxins
- Encourage regular physical activity to improve lung function and maintain a healthy weight
- Avoid exposure to allergens and toxins at work
- Practice good hygiene and get vaccinated to prevent respiratory infections
Conclusion
Asthma is a prevalent chronic respiratory condition that significantly impacts an individual’s quality of life.
It involves airway inflammation, leading to symptoms like coughing, difficulty breathing, and wheezing.
Asthma can be triggered by tobacco smoke, air pollution, genetics, and respiratory infections.
Different types of asthma exist based on triggers, such as allergic asthma and exercise-induced asthma.
Effective management includes identifying and avoiding triggers, using prescribed medications (like inhalers), and monitoring symptoms.
Preventive measures such as proper nutrition, exercise, and vaccinations can help minimize asthma exacerbations.
Early diagnosis and proper treatment allow individuals to lead active lives, making it crucial to raise awareness about asthma prevention, diagnosis, and management to improve outcomes and reduce associated risks.