
KATHMANDU: A urinary tract infection (UTI), one of the most common infections worldwide, can sometimes escalate from a mild issue to severe kidney damage if left untreated.
Affecting the urinary system, including the bladder, kidneys, urethra, and ureters, UTIs are often caused by bacteria, though they can also be triggered by fungi or, in rare cases, viruses.
Causes and Risk Factors
The most frequent cause of UTIs is the bacteria Escherichia coli, which attaches to the urinary tract and causes inflammation.
Other common pathogens include Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterococcus faecalis, and Proteus mirabilis.
Factors that increase the risk of developing a UTI include poor hygiene, dehydration, urinary catheters, and low immunity.
Women, particularly those who are sexually active or pregnant, are more likely to experience UTIs due to anatomical differences, such as a shorter urethra and its proximity to the anus, making it easier for bacteria to enter the urinary tract.
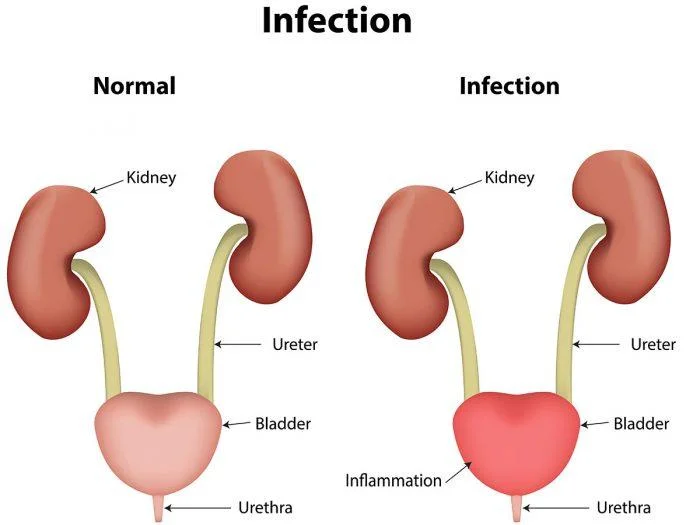
Types of Urinary Tract Infections
UTIs can affect different parts of the urinary tract, and symptoms vary depending on the area of infection:
Urethritis (Urethra): Discharge and burning during urination.
Cystitis (Bladder): Frequent urination, pain, and possibly blood in the urine.
Pyelonephritis (Kidney): Symptoms include fever, chills, nausea, vomiting, and pain in the back or side.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Common symptoms of lower UTI include burning with urination, frequent urination, cloudy urine, and pelvic pain in women or rectal pain in men. Upper UTI symptoms can involve fever, chills, fatigue, and nausea.
Diagnosing a UTI generally involves a physical examination, urine tests, and sometimes imaging tests like ultrasound or CT scans.
Treatment UTIs are typically treated with antibiotics if caused by bacteria. Antifungals and antivirals are used for fungal and viral infections, respectively.
Popular antibiotics for UTIs include Amoxicillin, Ciprofloxacin, and Nitrofurantoin. For relief, drinking plenty of water and using a heating pad can help alleviate symptoms.
Complications of Untreated UTIs
While most UTIs are treatable, untreated infections can lead to serious complications, including repeated infections, kidney abscesses, and urosepsis (a severe infection spreading throughout the body).
In pregnant women, UTIs can lead to preterm delivery or low birth weight. Chronic kidney infections can lead to scarring and permanent kidney damage.
Prevention
Prevention of UTIs involves several steps, such as maintaining proper hygiene, drinking 6-8 glasses of water daily, and urinating after sexual intercourse.
Women should avoid using feminine hygiene sprays and scented douches that can irritate the urinary tract.
Staying hydrated and not holding urine for long periods can also significantly reduce the risk of developing a UTI.
Conclusion
Though urinary tract infections are common, especially in women, they can lead to severe complications if not addressed early. Awareness of the symptoms, timely medical intervention, and preventive measures like hydration and good hygiene can help minimize the risk of UTIs evolving into more serious kidney issues.