
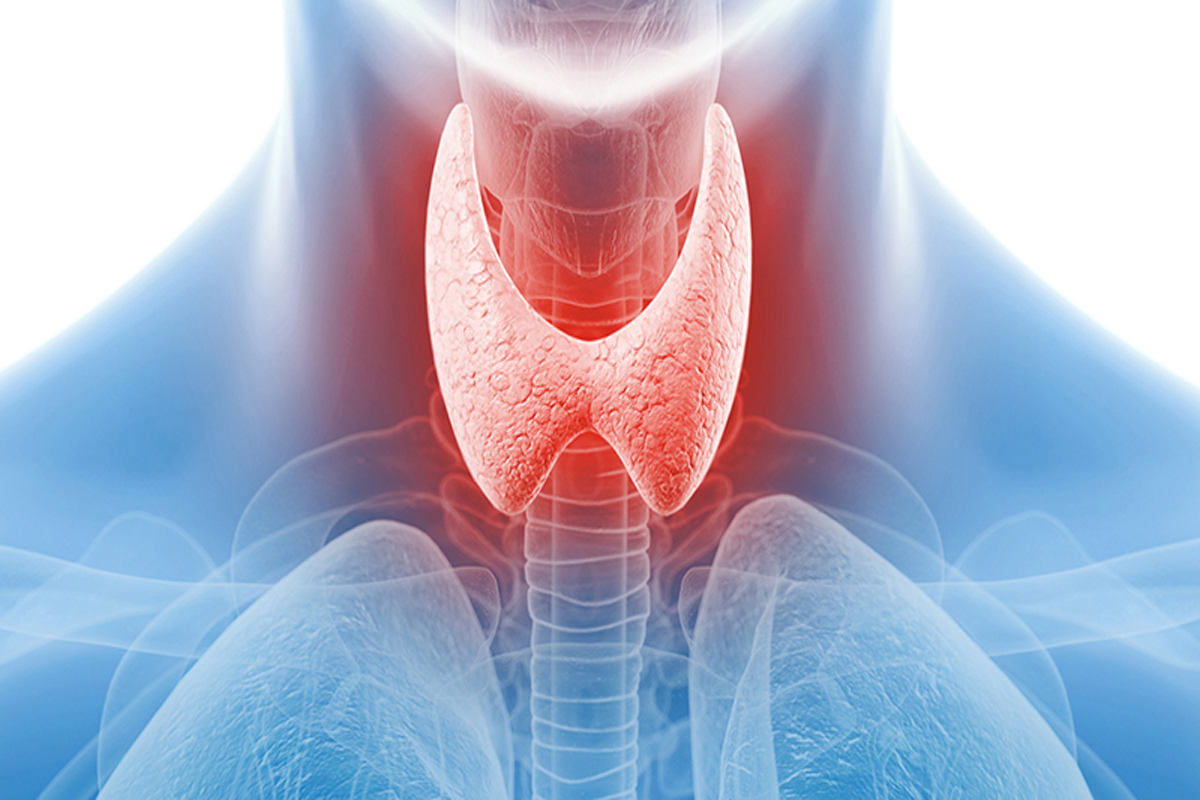
KATHMANDU: The thyroid is a small, butterfly-shaped gland located at the front of the neck, just below the Adam’s apple. Despite its size, the thyroid plays a vital role in regulating the body’s metabolism, energy levels, heart rate, body temperature, and overall growth and development. It does this by producing hormones known as thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3).
Problems with the thyroid usually occur when the gland produces too much hormone (hyperthyroidism) or too little hormone (hypothyroidism). In some cases, structural problems such as thyroid nodules or goiter may also develop.
When the thyroid is underactive (hypothyroidism), common symptoms include fatigue, weight gain, sensitivity to cold, dry skin, hair loss, constipation, depression, and slow heart rate. Women may experience irregular menstrual cycles, and children may show delayed growth or development.
An overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism) can cause symptoms such as unexplained weight loss, rapid or irregular heartbeat, excessive sweating, nervousness, anxiety, tremors, heat intolerance, and difficulty sleeping. Increased appetite and frequent bowel movements are also common.
Structural thyroid problems may present as swelling or a lump in the neck, known as goiter. Some people may experience difficulty swallowing, hoarseness, or a feeling of tightness in the throat.
Health experts note that thyroid symptoms often develop gradually and may be mistaken for stress or other health conditions. Regular health check-ups and blood tests can help detect thyroid disorders early. Early diagnosis and proper treatment can effectively manage thyroid conditions and prevent long-term complications.